Our Technology
Smart Sensors
The I-ON products include different sensors specially developed by Alteria Automation that in real time measure environmental variables such as levels of carbon dioxide, temperature, humidity, suspended particles, and air pollution. In addition, the sensors measure the levels of UV-C radiation.
Through an algorithm that measures the information from the sensors at all times, the irradiation process is adjusted. In this way, the effectiveness of the disinfection process is guaranteed. In other manufacturers’ equipment, the outcome of the process is unknown.
Likewise, I-ON, even in the unlikely event of a deviation from the standards that would prevent the disinfection cycle from being carried out correctly, activates an alarm message to the user that provides advanced predictive maintenance before a failure occurs.
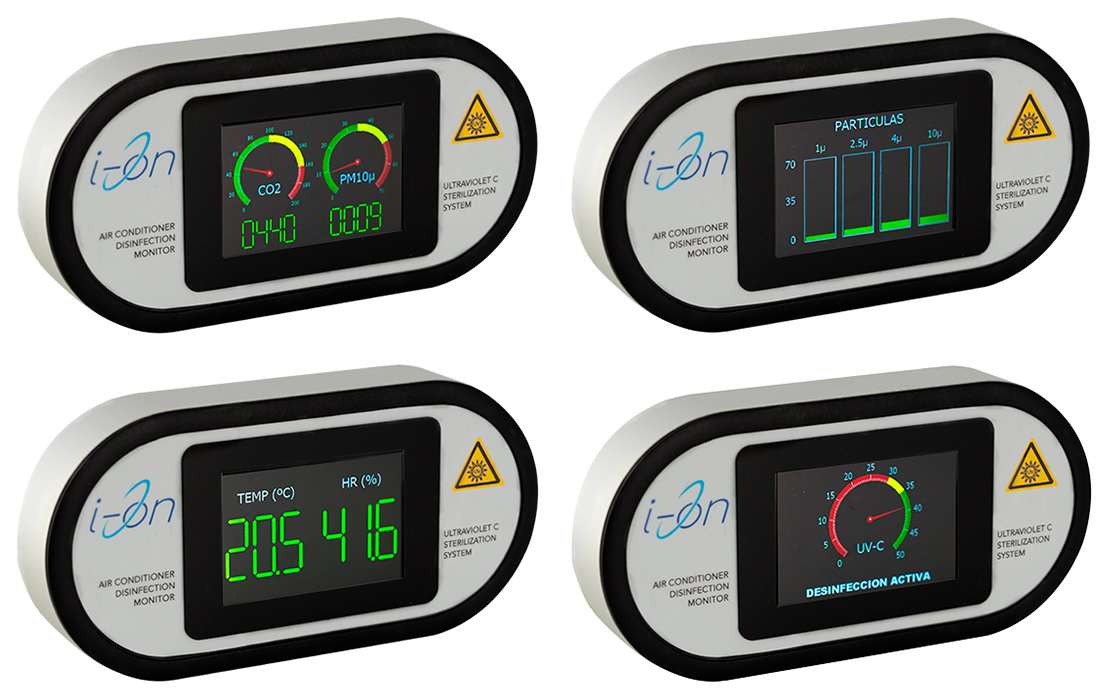


Traceability in real time
I-ON is the solution that has answered one of the biggest problems related to the disinfection process.
Hospitals, offices, factories, educational centers, residences for the elderly, restaurants, shopping centers, areas for events, theaters, cinemas, sports centers, among other spaces.
The question is always the same:
Are the premises truly sanitized?
Confirming that the disinfection process was successful is as important as doing it. It is useless to purchase disinfection equipment if its results are unknown. I-ON’s real-time traceability is unique. The data from the disinfection process is automatically transmitted to a cloud server to provide process traceability.
Internationally recognized disinfection technology
UV-C and ozone disinfection is recommended by international organizations such as WHO, EPA (American Environment Agency) and the Spanish Ministry of Health, among other organizations, for use against airborne infections.
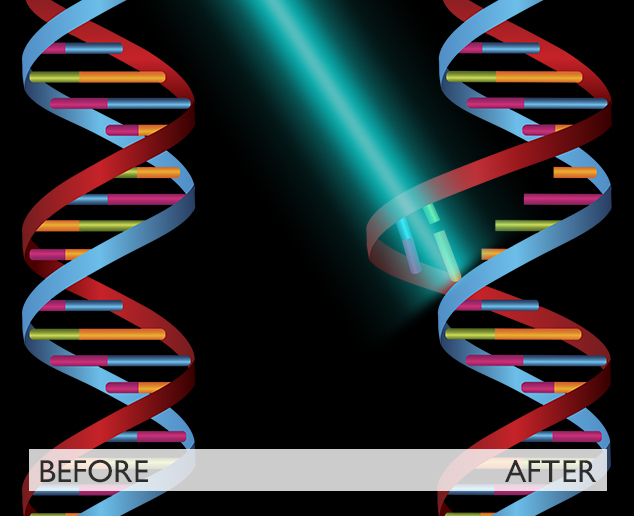

UV-C disinfection
The destructive effects of deep-field Ultraviolet radiation (UV-C) have been known since 1928.
Ultraviolet energy causes alteration of the Uracil bonds, one of the components of RNA viruses (Coronavirus).
The process called dimerization prevents the reproduction of the virus, annulling the infection process, which depends on the multiplication of the virus by attaching itself to a host cell.
The image represents the dimerization of Uracil in the RNA of a virus produced by UV-C radiation.

UV-C + Ozone disinfection
In the emissions of ultraviolet wavelengths of between175 and 210 nm the air is heavily ionized. The photon energy level is so high that the molecular structure of air breaks down and separates into positive ions and electrons.
This effect creates Ozone O3 gas molecules, made up of 3 unstable oxygen atoms that tend to capture electrons from any compound that comes close to it in order to regain its stability. Hence its high oxidative and disinfecting power.
In this way, ozone destroys the membrane that surrounds the nucleus of viruses and bacteria.

UV-C + Ionization disinfection
An ion is a molecule that has altered its natural charge. It is charged because the number of electrons does not match the number of stable protons.
An ion is a highly unstable radical and a very reactive particle that easily combines with almost anything around it.
The process of ionization of the air produces changes in the electro chemistry of suspended particles. Ionization destroys pathogens, including viruses and bacteria, by disrupting the cell membrane.
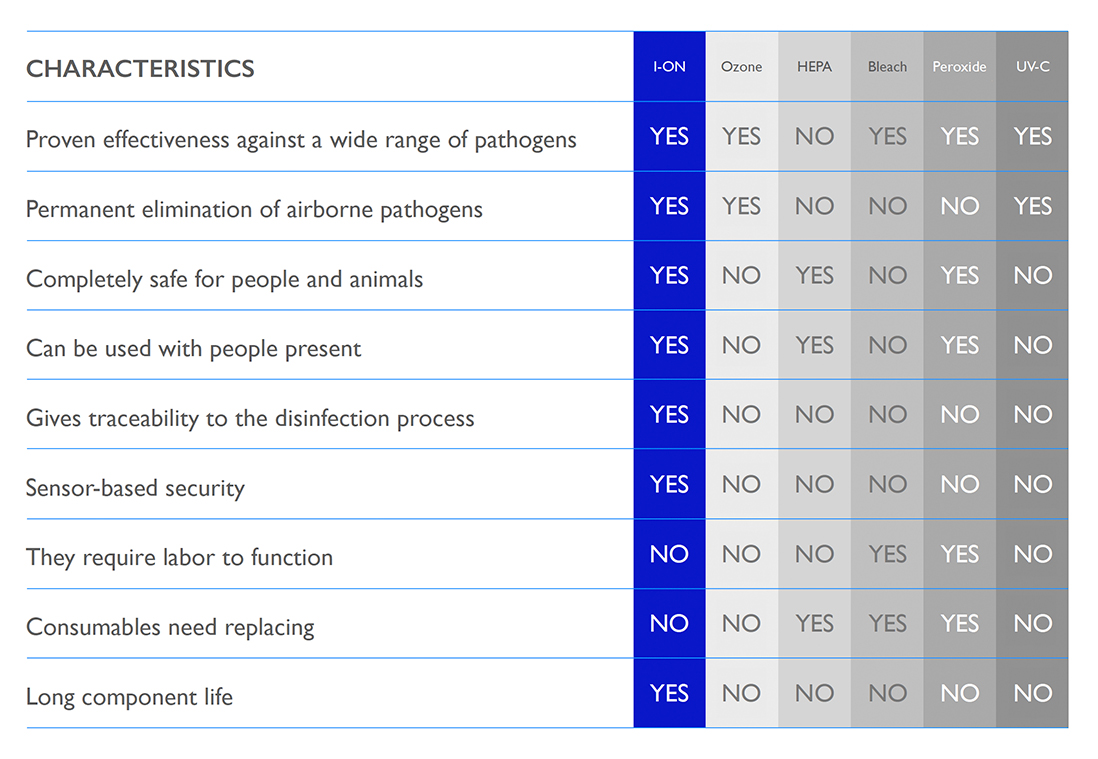
I-ON vs other disinfection systems